
Table of Contents
Introduction
Epilepsy is a neurological condition that influences a large number of individuals around the world. One of the most conspicuous parts of epilepsy is the “epilepsy assault,” which is generally alluded to as a seizure. These episodes can be startling to observe, however understanding what occurs during an epilepsy assault is significant for offering help and care to the individuals who experience them. In this blog, we’ll investigate epilepsy assaults in a human-accommodating and empathetic tone, revealing insight into what they are, what causes them, and how to help somebody during a seizure.
What Is an Epilepsy Attack?
An epilepsy assault, or seizure, is an unexpected, uncontrolled electrical aggravation in the mind. This unsettling influence can prompt a great many physical and close to home side effects, which differ from one individual to another.
Category of Epilepsy Attack
Epilepsy attacks can be categorized into two main types:
focal (partial) seizures and generalized seizures.
Focal (Partial) Seizures:
- These seizures begin in a particular region of the mind.
- They might be related with changes in awareness, feelings, or sensations.
- Contingent upon the particular region impacted, the individual encountering a central seizure might have side effects like jerking, tedious developments, or surprising sensations in a single piece of the body.
Generalized Seizures:
- Generalized seizures involve abnormal electrical activity throughout the entire brain.
- They often result in loss of consciousness and more noticeable physical symptoms, like convulsions, stiffening, or sudden falling.
The experience of an epilepsy assault can be startling, for the individual going through it as well as for everyone around them. In any case, it’s memorable’s vital that seizures are an ailment, not an impression of an individual’s personality or an indication of psychological maladjustment.
Recognizing Epilepsy Attacks
Recognizing epilepsy attacks is essential for timely intervention and support. Understanding the symptoms and triggers can be beneficial.

Symptoms
Symptoms of epilepsy attacks can vary but may include:
- Uncontrolled movements
- Loss of awareness
- Staring spells
- Sensory disturbances
Triggers
Identifying potential triggers for seizures is crucial. These triggers can include:
- Lack of sleep
- Stress
- Flashing lights
- Alcohol or drug use
Causes of Epilepsy Attacks
Epilepsy assaults are normally the consequence of a basic condition or trigger. It’s memorable’s essential that having a solitary seizure doesn’t be guaranteed to mean somebody has epilepsy. Epilepsy is analyzed when an individual encounters repetitive seizures. A few normal causes and triggers of epilepsy assaults incorporate:
Genetics: A family history of epilepsy can increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
Brain Injury: Head injuries, strokes, or brain tumors can damage brain tissue and lead to seizures.
Infections: Certain infections like meningitis or encephalitis can trigger seizures.
Developmental Disorders: Conditions like autism and neurofibromatosis may increase the risk of epilepsy.
Metabolic Disorders: Imbalances in blood sugar, sodium, or other chemicals can provoke seizures.
Drug and Alcohol Abuse: The use of certain substances can lower the seizure threshold.
Febrile Seizures: These are common in children and are often associated with high fevers.
: In some cases, no specific cause can be identified, and it’s referred to as idiopathic epilepsy.
Managing Epilepsy Attacks
Living with epilepsy and managing the risk of seizures can be a daily challenge. However, many individuals with epilepsy lead fulfilling lives by taking certain precautions and working closely with healthcare professionals. Here are some key steps in managing epilepsy:
Medication: Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are often prescribed to help control seizures. It’s crucial to take these medications as prescribed and regularly follow up with your healthcare provider to monitor their effectiveness.
Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, reducing stress, and avoiding known triggers can help minimize the risk of seizures.
Seizure Action Plan: Creating a seizure action plan with your healthcare provider can be valuable in case a seizure occurs. This plan outlines steps for you and your loved ones to take during a seizure.
Support System: Building a strong support network of friends and family who understand epilepsy and can provide assistance when needed is essential.
Education: Educating yourself and your loved ones about epilepsy can help reduce fear and misunderstandings surrounding the condition.
Safety Precautions: Taking precautions, such as not swimming alone, wearing a medical alert bracelet, and avoiding activities with a high risk of injury, can enhance safety.
Supporting Someone During an Epilepsy Attack
Being there for someone experiencing an epilepsy attack can make a significant difference in their well-being and recovery. Here are some essential tips to help you provide support:
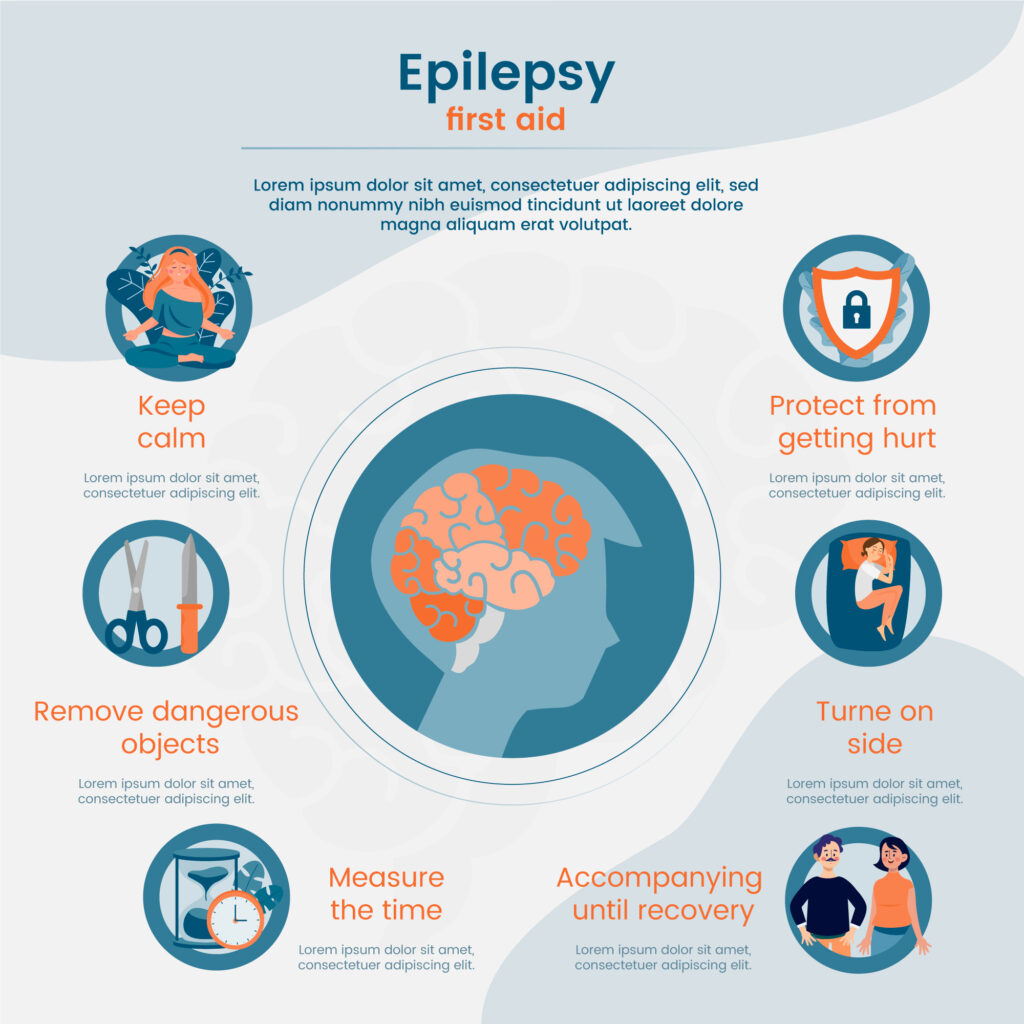
Stay Calm: It’s natural to feel anxious, but try to stay calm. Most seizures are short and resolve on their own.
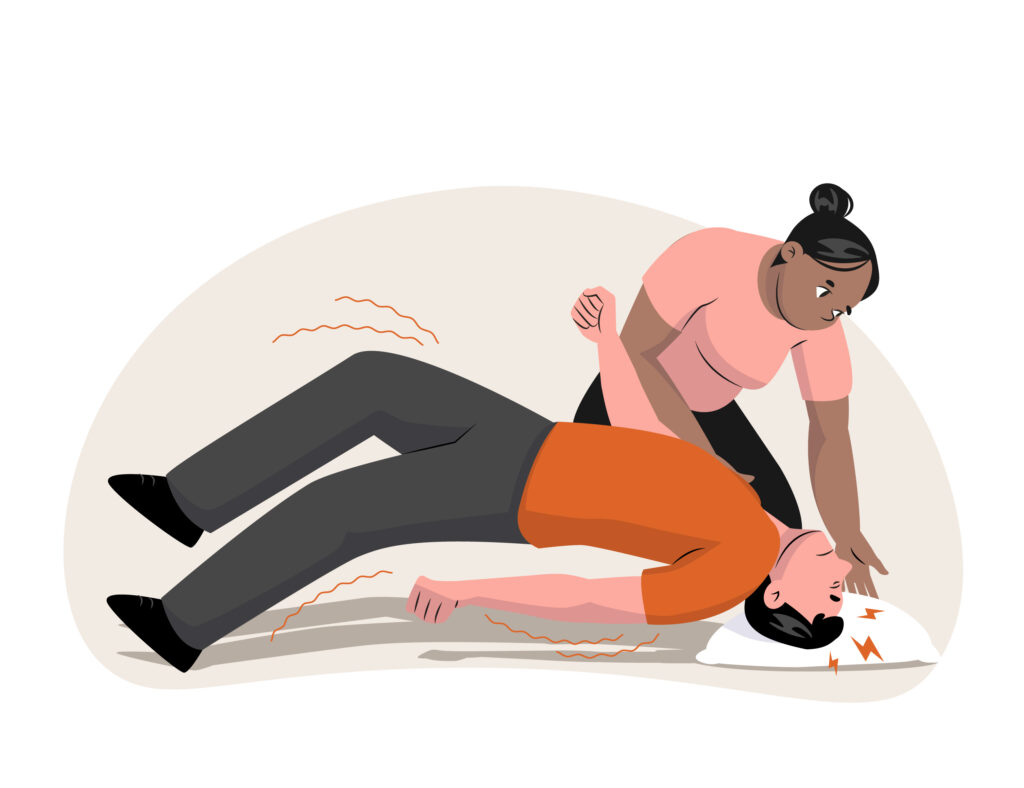
Ensure Safety: Help the person to the ground if they are not already there to prevent injury. Remove any nearby objects that could be harmful during the seizure.
Protect the Head: Gently cushion the person’s head with a soft object, such as a folded jacket, to prevent head injury.
Time the Seizure: Note the start time of the seizure. If the seizure lasts longer than five minutes, call for medical assistance.
Don’t Restrain: Avoid holding the person down or putting anything in their mouth during the seizure. It won’t stop the seizure and could cause harm.
Turn to the Side: Gently roll the person onto their side to help clear their airway and prevent choking if there’s excessive saliva or vomiting.
Comfort Afterward: Once the seizure is over, provide reassurance and support. The person may feel disoriented, tired, or confused.
Offer Privacy: After the seizure, give the person some space and privacy to recover, as they may be embarrassed or uncomfortable.

When to Seek Medical Help
Generally speaking, seizures end all alone, and the individual recovers awareness with practically no further issues. Nonetheless, there are circumstances where quick clinical consideration is important:
- If the seizure lasts longer than five minutes.
- If the person has difficulty breathing or appears to be in distress.
- If the person experiences a second seizure shortly after the first.
- If the person is pregnant, injured, or has a known medical condition.
In these instances, call 911 or your local emergency number for assistance.

Living with Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a lifelong condition for many, and learning to manage it is an ongoing process. Here are some insights to help individuals with epilepsy navigate their daily lives:
Medication Management: Many individuals with epilepsy expect medicine to control their seizures. It’s pivotal to accept meds as recommended and speak with a medical care supplier about any secondary effects or concerns.
Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help manage epilepsy. This includes getting enough sleep, managing stress, and avoiding triggers like excessive alcohol or drug use.
Seizure Diaries: Keeping a record of seizures can help identify patterns and triggers, aiding in better seizure control.
Support System: Building a strong support system of friends and family who understand epilepsy can provide emotional and practical support.
Driving and Employment: Laws regarding driving and employment can vary, but it’s essential to understand the regulations in your area and follow them for everyone’s safety.
Self-Care: Self-care is vital for emotional well-being. Engaging in hobbies, exercise, and relaxation techniques can help reduce stress and improve overall quality of life.

Epilepsy Myths Debunked
There are a few misguided judgments encompassing epilepsy, and it’s essential to expose these fantasies to advance comprehension and lessen shame. Here are a few normal legends and the comparing bits of insight:
Myth: You can swallow your tongue during a seizure. Truth: It’s physically impossible to swallow your tongue. Placing objects in the mouth during a seizure can lead to injury.
Myth: Epilepsy is contagious. Truth: Epilepsy is not contagious. It’s a neurological condition, not an infectious disease.
Myth: Only children have epilepsy. Truth: Epilepsy can affect people of all ages, from children to seniors.
Myth: All seizures are the same. Truth: Seizures can manifest in various ways, with different symptoms and levels of severity.
Myth: People with epilepsy are intellectually impaired. Truth: Epilepsy does not determine a person’s intelligence or cognitive abilities. Many individuals with epilepsy lead successful and fulfilling lives.
Conclusion
Understanding epilepsy assaults and how to offer help during a seizure is significant for making a humane and comprehensive society. By scattering fantasies, offering assistance when required, and advancing a protected and tolerating climate, we can make life more straightforward for those living with epilepsy. Keep in mind, epilepsy is only one part of an individual’s life, and with the right consideration and backing, people with epilepsy can lead satisfying and significant lives.
FAQs
Is epilepsy a common condition?
- Epilepsy is more common than you might think. It affects approximately 1 in 26 people at some point in their lives.
Can epilepsy be cured?
- Epilepsy cannot be cured, but it can often be managed effectively with the right treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
Are all seizures a sign of epilepsy?
- No, not all seizures are related to epilepsy. Some seizures can be caused by other medical conditions or triggers.
What should I do if I witness someone having a seizure?
- Stay calm, ensure their safety, and time the seizure. If it lasts longer than 5 minutes, or if they have trouble breathing afterward, call for medical assistance.
Can stress trigger epilepsy attacks?
- Stress is a common trigger for seizures in some individuals with epilepsy. Managing stress is an essential part of coping with the condition.
You can also see the following post : Understanding Dog Epilepsy : A No. 1 Guide to Supporting Your Furry Friend

Pingback: Understanding Dog Epilepsy : A No. 1 Guide to Supporting Your Furry Friend - CREATIVE WEB-MANIA
I appreciate you sharing this blog post. Thanks Again. Cool.
Simply wish to say your article is as amazing The clearness in your post is just nice and i could assume youre an expert on this subject Well with your permission let me to grab your feed to keep updated with forthcoming post Thanks a million and please carry on the gratifying work
Fantastic site Lots of helpful information here I am sending it to some friends ans additionally sharing in delicious And of course thanks for your effort
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.